Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-08 Origin: Site








You can think of the epon olt as the main control spot in a passive optical network. It works as the optical line terminal for your network. It links the service provider to the people who use the network. The olt controls who can use the network. It brings all the traffic together. It helps keep the service good. In a passive optical network, the epon moves data and controls the network. Check the table below to see what an olt does:
Primary Function | Description |
|---|---|
Subscriber Management | Checks and allows users so only approved ONUs/ONTs can use the network. |
Traffic Management | Picks which traffic is most important to keep service good, especially for voice and video. |
Fault Detection & Reporting | Watches the network for problems and tells about issues so they can be fixed fast. |
Bandwidth Allocation | Shares bandwidth fairly between users so no one takes too much. |
Forwarding Engine | Sends and moves data between Ethernet and optical networks the right way. |
Network Management Interface | Gives tools for network admins to set up, watch, and manage the network. |
The EPON OLT is the main control center in a passive optical network. It manages how data moves and who can use the network.
It changes electrical signals into optical signals. It lets many users share one fiber line by using passive splitters.
EPON OLTs help give fast, fair, and steady internet. They do this by managing bandwidth, putting important data first, and finding problems.
There are two main types. Modular OLTs are for big, growing networks. Fixed OLTs are for smaller and simpler setups.
EPON technology gives solutions that can grow and save money. It works well in cities, suburbs, and rural places.
The epon olt sits at the center of a passive optical network. It means Ethernet Passive Optical Network Optical Line Terminal. You usually find it in the main office of your internet provider. The epon olt is the main link between the provider’s network and the fiber cables that go to homes or businesses. It changes electrical signals from the provider into optical signals for the fiber. It also changes optical signals back into electrical ones for the provider’s side.
The epon olt lets one point talk to many points. It sends data to many users at once. It also gets data from all users through one fiber. This way, many people can share the same fiber line. The epon olt uses passive splitters to share the signal with many users. This makes it possible to give internet, voice, and video over one network.
Note: The epon olt is more than just hardware. It is the main control for the whole epon system. It controls how data moves, who can use it, and how much bandwidth each person gets.
Here is a simple chart that shows where the epon olt fits in a passive optical network:
Network Element | Location | Main Function |
|---|---|---|
EPON OLT | Central Office | Changes signals, controls data, manages users |
Optical Splitter | Outside Plant | Shares optical signal with many users |
ONU/ONT | User Premises | Gets and sends data for end users |
The epon olt is very important in a passive optical network. It is like the backbone and main control for managing users and data. It links the provider’s main network to the fiber that goes to your area.
Here is what the epon olt does in a passive optical network:
It changes electrical signals from the provider into optical signals for the fiber.
It sends data to all users using passive splitters.
It gets data from users and puts it together for the provider.
It talks with each ONU or ONT at your place.
It shares bandwidth using special rules so everyone gets a fair amount.
It uses Logical Link IDs to know each user and keep data safe.
It checks the network, does maintenance, and fixes problems to keep your connection working.
The epon olt also works with other network parts. It connects to the Optical Distribution Network, which has all the fiber cables and splitters. It manages the ONUs and ONTs at people’s homes. The epon olt uses rules like IEEE 802.3ah for running and fixing the network. It works with the Network Access Server to set rules and keep service good.
Tip: Olt epon technology helps you grow your network easily. You can add more users by connecting more ONUs or ONTs without changing the main fiber.
The epon olt can give many services at the same time. It gives fast internet, voice calls, and video streaming over one fiber. It keeps delays low and makes sure everything works well, even when many people are online.
You see the epon olt as the main control in a passive optical network. It handles everything from changing signals to checking users. It keeps your connection fast, safe, and steady. The epon olt is why epon networks can serve many people with just one fiber line.
The epon olt helps move data fast and safely in the network. It connects to many onu devices using passive splitters. This setup lets many users send and get data at the same time. The epon olt uses Ethernet-based rules, so it is easy to use.
The epon olt follows the IEEE 802.3ah rule. This rule tells how data moves between the olt and each onu.
It gives the same speed for sending and getting data, up to 1.25 Gbps.
The epon olt changes electrical signals to optical signals for the fiber. It also changes them back for the provider.
It sends data in packets, which makes data flow smooth and flexible.
The epon olt works in a way where one olt can help many onu devices at once.
The epon olt sends data as light signals through the fiber. Each onu gets the data, decodes it, and sends it to your devices. This keeps your connection quick and steady.
Here is a table that shows the main data transmission features:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Protocol | IEEE 802.3ah (Ethernet-based) |
Transmission Rate | 1.25 Gbps up/down (symmetrical) |
Architecture | Point-to-multipoint via passive splitters |
Data Encapsulation | Optical signals over fiber, packet-based |
Integration | Simple with existing Ethernet networks |
The epon olt lets you get fast internet, voice, and video over the network. It is easy to grow and does not cost too much.
The epon olt controls every user on the network. It uses smart rules to make sure only allowed users can join. This keeps your network safe and neat.
The epon olt uses the Multi-Point Control Protocol to manage how each onu connects and sends data.
When a new onu wants to join, the olt starts a check. It sends a Discovery Gate message.
The onu answers with a Register Request. The olt gives that onu a Logical Link Identifier.
Each onu gets its own link. This stops data mix-ups and keeps your data safe.
The olt watches each onu’s status and manages how much data they need. It uses REPORT messages from the onu to know this.
The olt can use more checks to see if an onu is allowed to join. This makes the network even safer.
The epon olt keeps things neat by giving each user a special link. It also makes sure only trusted devices can join.
Here is a simple list of what the epon olt does for subscriber management:
Registers new onu devices and gives them special IDs.
Makes a private link for each user.
Watches how much data each user needs and changes resources.
Uses extra checks to keep out devices that should not join.
With these tools, the epon olt gives you a safe and smooth network.
Quality of Service is important for a good experience. The epon olt uses QoS to make sure important data goes first. You see this when you watch videos or make calls without problems.
The epon olt can tell what kind of data is being sent. It gives more importance to things like voice and video.
It uses dynamic bandwidth sharing. The olt listens to what each onu needs and changes the plan right away.
The olt sends GATE messages to tell each onu when to send data. This keeps things fair and smooth.
Newer epon systems use better ways to share resources. They can even give special signals to users who need more.
The epon olt helps you have clear calls, fast downloads, and smooth videos. It does this by sharing bandwidth and picking which data goes first.
Here is a quick look at QoS features in the epon olt:
QoS Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
Traffic Prioritization | Voice and video get higher priority |
Dynamic Bandwidth | Adjusts to real-time needs of each onu |
Low Delay and Jitter | Keeps streaming and calls smooth |
Remote Management | Lets you monitor and adjust QoS settings |
The epon olt gives you a steady network. It keeps your connection strong, even when lots of people are online. You get great service because the olt uses smart QoS controls to manage traffic and resources.
You see three main parts in every passive optical network using epon technology. Each part has a special job to help you get fast and reliable internet, voice, and video services.
Optical Line Terminal (OLT)
The olt sits at the central office. It acts as the main control for the whole epon system. You use it to manage bandwidth, assign time slots, and register each onu or ont. The olt sends data downstream to all users and collects upstream data from every onu.
Optical Network Unit (ONU) / Optical Network Terminal (ONT)
The onu or ont stays near your home or business. It changes optical signals from the fiber into electrical signals for your devices. It also sends your data back upstream to the olt. The onu waits for the olt to give permission before sending data, so you avoid collisions.
Optical Distribution Network (ODN)
The odn is the path that connects the olt to every onu and ont. It uses fiber cables, splitters, and connectors. The odn does not need power because it uses passive parts. It lets the olt send signals to many users at once.
You can think of the odn as the highway for light signals. It carries data between the olt and all the onu or ont devices.
Here is a table to help you see how each part works:
Component | Location | Main Role |
|---|---|---|
OLT | Central Office | Controls network, manages bandwidth, registers ONU/ONT |
ODN | In the Field | Connects OLT to ONU/ONT, splits signals, uses fiber |
ONU/ONT | User Premises | Converts signals, sends/receives user data |
You find that the olt, odn, and onu work together to make the passive optical network run smoothly. The olt sends data to all onu and ont devices using broadcast mode. Each onu checks the signal and takes only the data meant for it. The olt uses time division multiplexing to give each onu a turn to send data upstream. This keeps the network safe from data collisions.
The olt collects data from the core network and pushes it through the odn.
The odn uses fiber splitters to share the signal with many onu and ont devices.
Each onu or ont changes the light signal to electrical signals for your devices.
The onu arranges your data and sends it back to the olt in its assigned time slot.
The olt manages network security, configuration, and bandwidth for every user.
You see that the odn connects everything together. It uses fiber to reach long distances, sometimes up to 20 km. The quality of the odn affects how well your epon network works. If you want a strong and scalable passive optical network, you need good fiber and reliable splitters.
Tip: The epon system lets you add more users easily. You only need to connect more onu or ont devices to the odn. The olt will manage them without changing the main fiber setup.
You get internet, IPTV, and voice services through this setup. The olt, odn, and onu work as a team to deliver fast and safe data to your home or business.
A modular OLT is good if you want your network to grow. This type has a main box with slots for different cards. You can add or change cards as your network gets bigger. Modular OLTs work with many PON standards, like GPON, XG-PON, and XGS-PON. They give you lots of ways to expand and change your network. If you run a big city network or a busy business area, modular OLTs help you serve more people and services.
Modular OLTs have parts you can swap while the network is on. They also have two control boards and backup power. These things help your epon network keep working if something breaks.
Here is a table that shows how modular and fixed OLTs are different:
Feature | Fixed OLT | Modular OLT |
|---|---|---|
Scalability | Limited, fixed ports | Highly scalable, add modules as needed |
Flexibility | Less adaptable | Supports many PON types, easy upgrades |
Redundancy | Minimal | Dual boards, power, PON protection |
Uplink Capacity | 1G/10G | Up to 100G |
Management | Basic | Advanced, SNMP, web, CLI |
Use Case | Small, rural, simple networks | Large, urban, mission-critical networks |
A fixed OLT is a small box with a set number of ports. You use it for small networks or when you want something simple. Fixed OLTs work with both 1G and 10G epon boards. They connect to many onu types, like 1G and 10G models. You save money and can set it up easily. Fixed OLTs are great for homes, small offices, and places far from cities.
Fixed OLTs use splitters to let one port serve many onu.
They use TDMA so each onu gets a fair turn to send data.
Fixed OLTs use less energy and do not break often.
You see fixed OLTs in homes, schools, and small businesses. They are easy to use and work well.
You can find epon olt solutions in many places. Modular OLTs are best for big networks, like city internet, business parks, and data centers. You can use them for:
FTTH (Fiber to the Home) in apartments and neighborhoods.
FTTO (Fiber to the Office) for business buildings.
Mobile backhaul for cell towers.
Smart city projects, like traffic lights and cameras.
Rural broadband to reach faraway places.
Fixed OLTs are good for smaller jobs. You use them in:
Homes and small offices for internet, TV, and phone.
Schools and hospitals for fast, steady connections.
Campus wireless networks with one place to manage everything.
Both types let you connect many onu with just one fiber. You get fast and steady epon service for everyone.
The number of ports on an olt shows how many users you can connect. Each port connects to several ONUs using fiber splitters. If your epon olt has more ports, you can serve more homes or businesses. For example, an 8-port olt lets you add more people than a 4-port olt. This helps your network grow when more people want fast internet. More ports also help you share bandwidth better and handle more data. Some new models have fast uplinks, like 100Gbps, to make the network stronger. If you pick an olt with enough ports, your network will be ready for more users and you can save money as you grow.
You may wonder how fast your epon network can send data. EPON OLTs usually give the same speed for downloads and uploads. Most models can go up to 1.25 Gbps both ways, but real speed is about 1 Gbps after coding. This is good for most homes and small businesses. If you look at GPON, it can go faster, especially for downloads. Here is a table to show the difference:
Technology | Downstream Rate | Upstream Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
EPON | 1.25 Gbps (1 Gbps actual) | 1.25 Gbps (1 Gbps actual) | Symmetrical, uses 8b/10b coding |
GPON | Up to 2.5 Gbps | Up to 1.25 Gbps | Asymmetrical, more flexible |
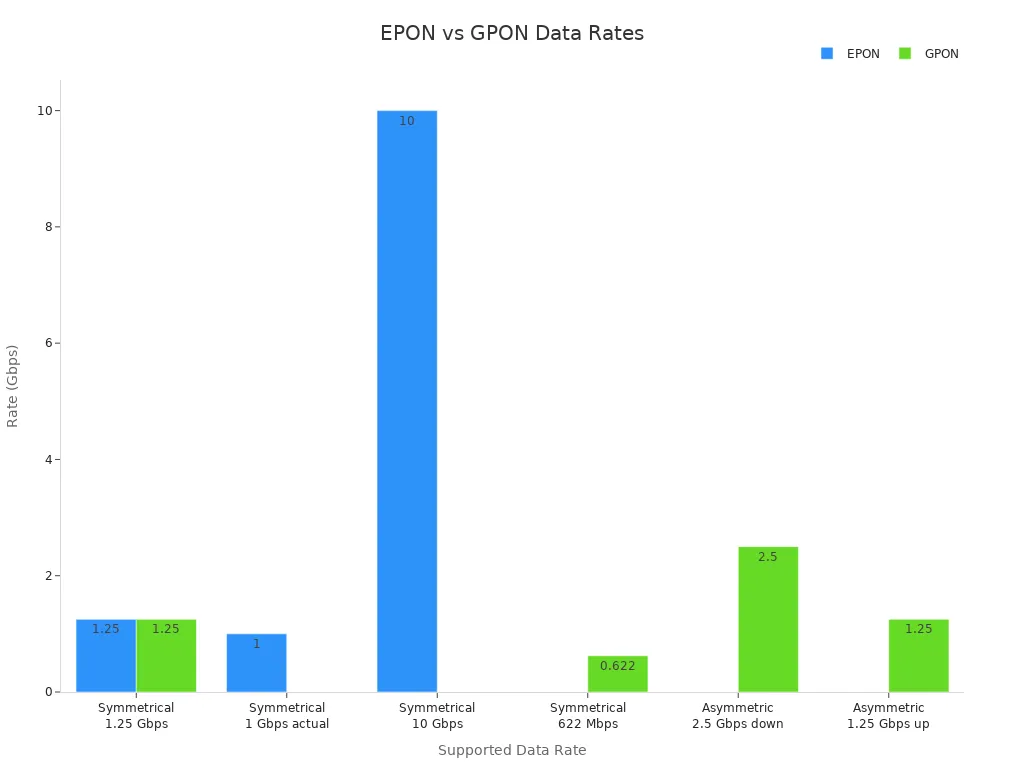
You can see that epon gives steady and equal speeds both ways, which works well for most people.
You need good tools to keep your epon network working well. OLTs let you control and watch your system in many ways. You can use a web page, command line, or remote access with SSH or HTTPS. Here are some things you can do:
Watch and set up your network from anywhere
Update the system and firmware easily
Use alarms and logs to find problems fast
Use VLANs to manage your network in different ways
Keep your network safe with secure logins and access
These tools help you fix problems quickly, keep your network safe, and make changes without going to the site. You save time and keep your fiber network strong.
You want your epon network to work all the time. OLTs have features to keep your service running, even if something breaks. Here are some ways they do this:
Extra power supplies keep the olt on if one stops
Backup boards take over if the main board fails
You can change power or fans without turning off the system
Good monitoring tools help you find and fix problems fast
Strong parts and energy-saving chips make the olt last longer
These features protect your network and keep it working, even during repairs or upgrades.
You can make your network bigger with epon technology. One OLT can help lots of users. It supports high split ratios, like 1:64 or 1:128. This means one device connects many homes or businesses. The OLT gives each user their own bandwidth and data. Everyone gets a steady connection. You get features like dynamic bandwidth allocation. This keeps things fair and fast. Advanced error correction helps keep your data safe. It also lowers packet loss. A wide optical budget lets you reach users far away. Sometimes, you can go over 20 kilometers. This makes epon good for big cities and country areas. You can add new services, like 4K streaming and cloud computing, as your network grows.
High split ratios let one OLT help many users.
Dynamic bandwidth allocation keeps things fair and quick.
Advanced error correction keeps your data safe.
Wide optical budget lets fiber go long distances.
Scalable design helps you give more people fast internet.
Epon networks help you save money. The system uses passive optical splitters. These do not need power or much fixing. This lowers your costs. Fiber and equipment prices keep dropping. Building your network gets cheaper over time. You use less space and power in server rooms. The simple two-tier setup makes things easy to manage. You do not need extra protocol conversion. This lowers complexity and cost. EPON lets you offer more services, like fast internet and video. This helps you earn more and balance your spending.
Passive splitters lower fixing and power needs.
Equipment costs drop as tech gets better.
Simple network saves time and money.
Flexible design lets you change network size.
Ethernet support lowers extra costs.
You can use epon OLTs in many places. In cities, splitters are in the central office. Fiber goes straight to each user. This works well for crowded areas. In country areas, splitters are along roads or near homes. Sometimes, remote OLTs hang on poles or wires. This helps reach faraway users. These setups match the network to the area’s needs. City networks cover short distances with lots of users. Country networks reach farther with fewer users. EPON OLTs work for both, so you can build networks anywhere.
Deployment Scenario | Typical Max Distance | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Urban FTTH (dense areas) | Up to 5 km | Short reach, high split ratio |
Suburban neighborhoods | 5 to 15 km | Moderate attenuation |
Rural PON deployment | 15 to 20 km | Longer distances, fewer users |
Special long-haul GPON | 20 to 40+ km | Needs advanced optics, costly |
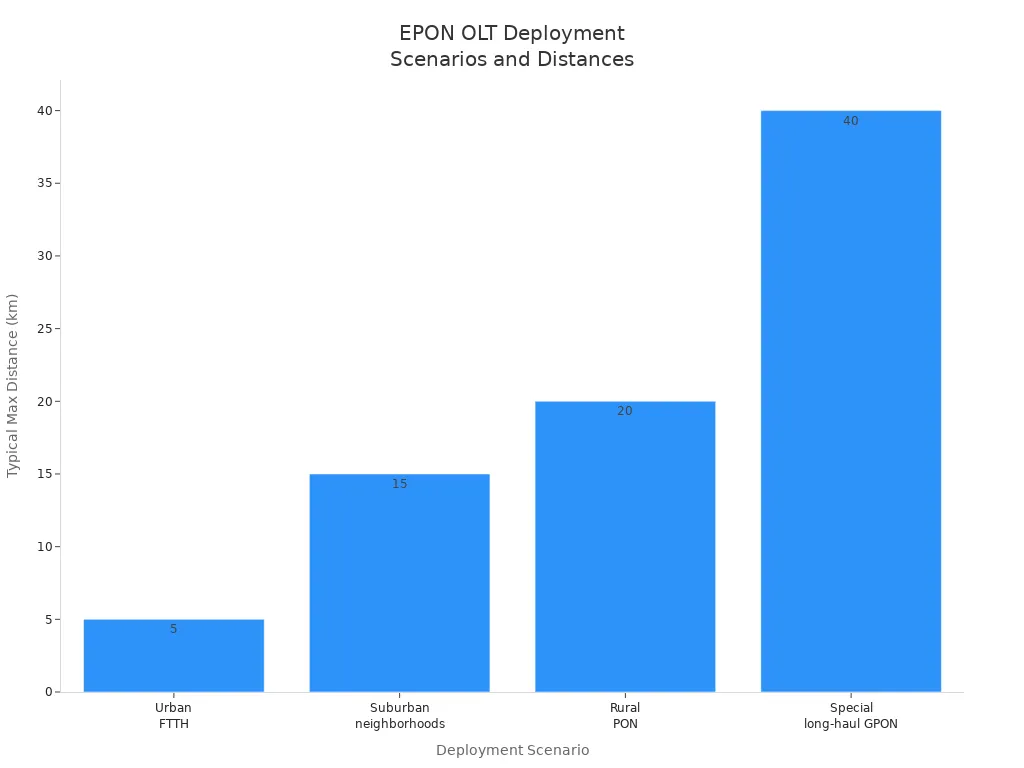
You see epon OLTs help bring fast internet to many places. Telecom companies use them to upgrade networks. They meet the need for faster fiber connections. Governments invest in broadband and smart city projects. Epon is a big part of digital growth around the world.
You play a key role in building a strong passive optical network. EPON OLTs help you manage users, control bandwidth, and keep your network reliable. When you plan your network, remember to:
Choose OLTs that match your service needs and support the right boards.
Check port counts, power needs, and hardware features for future growth.
Plan your cable layout and splitter locations to save costs and reach more users.
A well-chosen EPON OLT lets your passive optical network deliver fast, stable service for everyone.
You use an EPON OLT to connect many homes or businesses to the internet. It manages data, controls who joins, and keeps your connection stable. It sends and receives signals between your provider and your devices.
You can connect many users with one EPON OLT. Most models let you link up to 64 or 128 ONUs per port. If you add more ports, you reach even more people. This helps you grow your network easily.
Modular EPON OLTs let you add or change parts as your network grows. Fixed EPON OLTs have a set number of ports and work best for small setups. You pick modular for big networks and fixed for simple ones.
You use web pages, command lines, or remote tools to manage your EPON OLT. You can check status, set up users, and fix problems from anywhere. Alerts and logs help you find issues quickly.
People often ask about how many users an OLT supports, how to set up ONUs, and what makes EPON different from GPON. You also want to know about speed, reliability, and how to expand your network.