Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-28 Origin: Site








GPON means Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It gives fast internet to homes and businesses using fiber cables. GPON uses a PON structure. Both GPON and EPON use an optical line terminal, called OLT, at the provider’s side. They also use ONUs or ONTs at the user’s place. EPON OLT controls connections in EPON networks. GPON OLT can handle more users and faster speeds. The big difference is in how they send data. GPON shares bandwidth faster and better. Both GPON and EPON give strong and flexible network solutions for homes and companies.
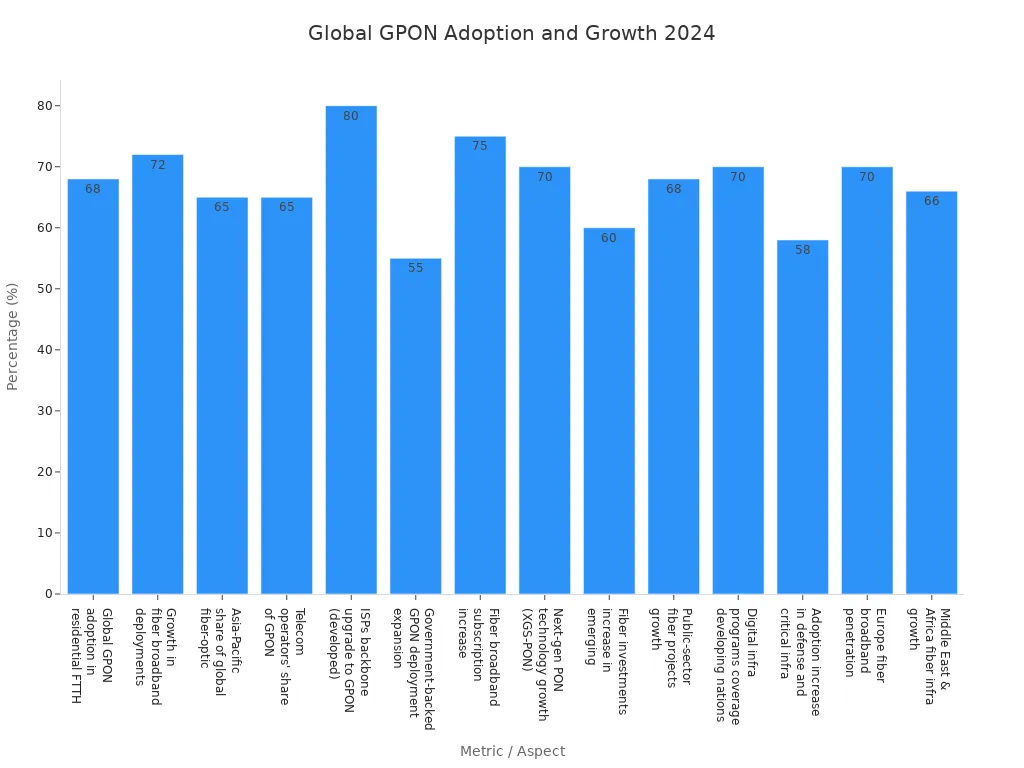
Metric / Aspect | Value / Percentage | Description / Context |
|---|---|---|
Global GPON adoption in residential FTTH deployments | 68% | Shows how much GPON is used in home fiber networks around the world in 2024. |
Growth in fiber broadband deployments | 72% | Tells how much fiber broadband is growing worldwide, helping GPON use. |
Asia-Pacific share of global fiber-optic installations | 65% | Shows that Asia-Pacific leads in fiber-optic networks using GPON. |
GPON gives faster download and upload speeds than EPON.
GPON OLT uses smart protocols to share bandwidth well.
EPON OLT is easier to set up for Ethernet networks.
Both use PON design for safe and flexible data delivery.
GPON gives fast internet, phone, and TV with one fiber cable. This makes it great for homes and businesses.
The main parts of GPON are the OLT at the provider. There are passive splitters that share signals. ONT and ONU devices are at users’ places.
GPON lets many users share one fiber. It saves money by using passive equipment. It can reach far, up to 20 kilometers or more.
It gives high speeds up to 2.5 Gbps for downloads. Upload speeds can be up to 1.25 Gbps. It keeps data safe with encryption and user checks.
GPON can grow to help more users easily. It works well for fiber to homes, buildings, and big networks. This makes it ready for the future.
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It is a kind of PON. It gives fast internet, phone, and TV using fiber-optic cables. GPON follows ITU-T G.984.x rules. These rules tell how it should work. This system can support up to 128 users on one fiber. It can reach about 20 kilometers. GPON uses a point-to-multipoint setup. One fiber from the provider can serve many homes or businesses.
Note: GPON uses wavelength division multiplexing. It sends data downstream at 1490 nm. It sends data upstream at 1310 nm. This helps it move lots of data at the same time.
GPON is made for triple-play services. It can give internet, phone, and TV with one fiber. The system uses a passive optical network. There are no powered devices between the provider and the user. This keeps costs low. It also makes the network strong.
Here are some important facts about GPON:
It uses ITU-T G.984.x rules.
It supports 64 to 128 users on one fiber.
It can reach up to 20 km from the provider.
It uses passive optical splitters in the network.
It gives triple-play services (internet, phone, TV).
It works with FTTx setups like FTTH, FTTC, and FTTN.
It uses GEM and ATM for data framing.
It can use RF overlay for cable TV.
A GPON network has a few main parts. Each part helps users get fast and steady service.
Component | Location | Main Functions |
|---|---|---|
OLT (Optical Line Terminal) | Service provider’s central office | Controls the whole PON network, manages bandwidth, connects to the core network, and sends data to users. |
Passive Optical Splitter | In the distribution network | Splits the optical signal from the OLT to many users without needing power. |
ONU/ONT (Optical Network Unit/Terminal) | User’s home or business | Changes optical signals to electrical signals for devices like computers, phones, and TVs. |
OLT: This device is at the provider’s office. It is the brain of the PON. The OLT decides how much bandwidth each user gets. It collects data from all users. It sends data to the main network. It also sends data back to users. The OLT keeps the network safe with encryption and user checks.
Passive Optical Splitter: This small device splits one fiber into many. It does not need power. This makes it very reliable. The splitter lets the OLT talk to many ONUs or ONTs at once.
ONU/ONT: This box is in the user’s home or office. It takes the light signal from the fiber. It turns it into something devices can use. Some ONUs or ONTs have extra features. These can be Wi-Fi, phone ports, or security tools.
Tip: ONT and ONU mean almost the same thing. ONT is used for home setups. ONU can mean any user-side device.
Optical-to-electrical converter
Data and voice processing units
Ethernet ports for computers and routers
Power supply (adapter or PoE)
Status lights and buttons
Optional: Wi-Fi, VoIP, and security features
A GPON network uses these parts to give fast internet and other services to many users. The PON design keeps the system simple and cheap.
GPON uses a point-to-multipoint setup. One fiber from the provider connects many places. The system follows ITU-T G.984 rules. The main parts are the OLT, ONT, and passive optical splitters. The OLT is at the provider’s office. It is the end of the network. It sends data to users and controls connections. The ONT is at the user’s place. It changes light signals into data for devices. Passive optical splitters share the signal with many users. This design keeps costs low and helps the network grow easily.
Here is a table that lists the main parts of GPON architecture:
Architectural Element | Description |
|---|---|
Standard | ITU-T G.984 sets GPON rules and details |
Network Type | Point-to-multipoint fiber optic access network |
Optical Fiber | Single mode fiber (ITU-T G.652) from OLT to ONTs |
Optical Line Terminal (OLT) | At provider’s office, works as the network’s end |
Optical Network Terminal (ONT) | At user’s place, marks the network’s edge, often has home gateway and phone services |
Passive Optical Splitters | Split the signal for many users, split ratios like 1:32 or 1:64 |
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) | Downstream at 1490 nm, upstream at 1310 nm |
Bandwidth | Downstream: about 2.5 Gbps; Upstream: about 1.25 Gbps |
Reach | Can go up to 20-40 km, depends on split ratio and fiber quality |
Split Ratio | Usually 1:32 or 1:64; can be stacked for bigger areas |
Network Topology | Tree shape made by splitters |
Optical Power Budget | About 28 dB loss allowed, so it can reach far |
Additional Features | Has FEC, dynamic bandwidth sharing, and QoS |
Outside Plant (OSP) | Passive, so it needs less fixing |
GPON uses a tree-shaped network. The OLT links to many ONTs with splitters. The network gives fast speeds and can go far. It can reach up to 40 kilometers if the split ratio is right. The passive outside plant means less fixing and lower costs.
GPON sends data both ways. The OLT sends data down to all ONTs. Each ONT takes only the data for its user. The ONT turns the light signal into electrical signals for things like computers and phones. The ONT sends data back up to the OLT. The OLT gathers this data and sends it to the main network.
The OLT is the main spot for data. It sends and gets info from users.
Downstream data goes from the OLT to ONTs using splitters.
Each ONT only reads its own data.
Upstream data goes from ONTs back to the OLT. The OLT controls how much bandwidth each ONT uses.
The network uses burst transmission for upstream data. This lets many users share one fiber.
The passive optical network means no powered devices between the OLT and ONTs.
GPON uses wavelength division multiplexing. Downstream data goes at 1490 nm. Upstream data goes at 1310 nm. This lets the network send and get data at the same time. The OLT manages the flow and keeps the network safe and working well.
GPON gives users very fast internet. It can download at up to 2.5 Gbps. Upload speeds can reach 1.25 Gbps. This means you can stream videos and play games easily. You can also use cloud services with no lag. Download speeds are higher than upload speeds. This is called an asymmetric model. GPON ONT devices move lots of data quickly. They are good for homes and businesses that need more internet.
Specification | GPON |
|---|---|
Downstream Speed | Up to 2.5 Gbps |
Upstream Speed | Up to 1.25 Gbps |
Symmetry | Asymmetric |
GPON networks use wavelength division multiplexing. This lets them send data both ways at once. It helps many devices work at the same time in one home or office.
GPON can grow to serve more users. It uses a point-to-multipoint setup. One OLT port can connect to many people with splitters. This makes it easy to add new users. Technicians just connect them to a splitter. They do not need to put in new fiber. Ethernet networks need a line for each user. GPON saves time and money.
Feature | Active Optical Network (AON) | Passive Optical Network (PON - GPON) |
|---|---|---|
Users per OLT Port | 1 | 32, 64, or up to 128 |
Scalability | Limited | High |
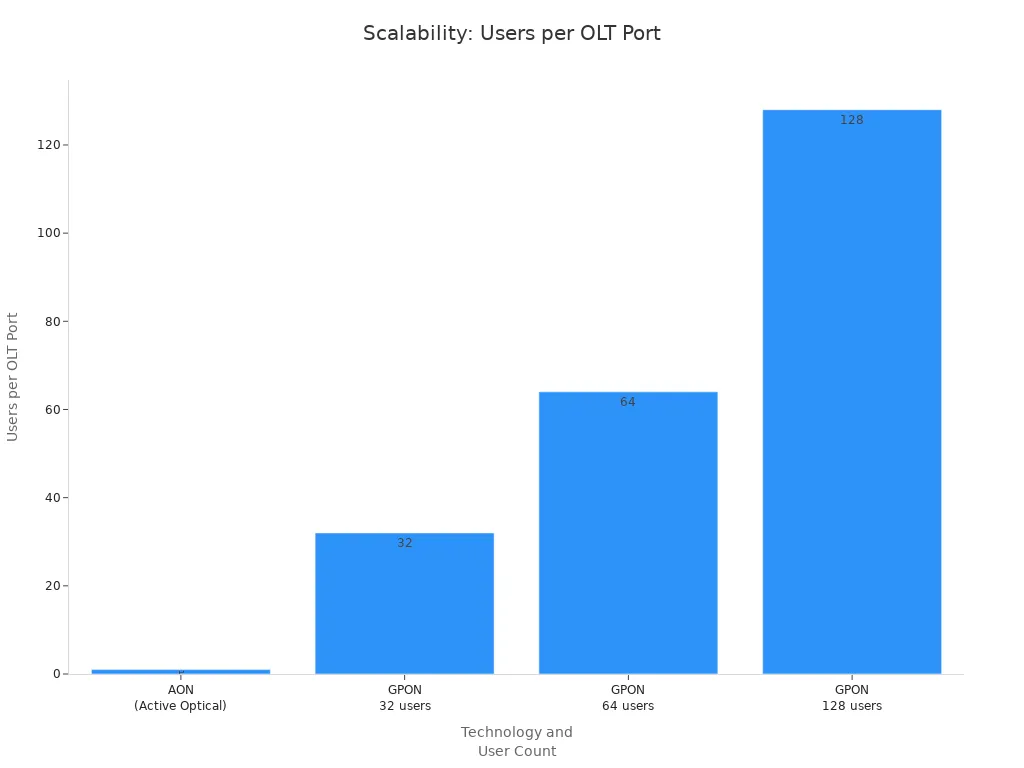
If more people need internet, GPON can upgrade. Newer types like XGS-PON and NG-PON2 give even faster speeds and support more users.
GPON networks keep your data safe. They use AES encryption to stop hackers. Each ONU must prove who it is with a serial number and password. The network uses VLANs to keep user groups apart. This makes it hard for outsiders to get private data. Central control helps fix problems fast. Fiber cables are hard to tap, so they are safer.
Providers use strong passwords and update the network often. They watch for threats all the time to keep it safe.
AES encryption keeps data safe between OLT and ONUs.
Authentication stops people who should not get in.
VLANs keep user groups apart.
Central control helps fix problems fast.
Fiber cables are safer than copper wires.
Security Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
Encryption (AES) | Keeps data safe between OLT and ONUs. |
Authentication | Checks ONUs with serial numbers and passwords. |
Network Segmentation | Uses VLANs to keep users apart. |
Centralized Management | Watches and enforces security rules. |
Physical Security | Fiber is harder to tap than copper. |
The EPON OLT is the main control in an EPON network. It is at the provider’s office. This device manages all data between the main network and users. The EPON OLT does many jobs to keep things working well.
Here is a table that lists what the EPON OLT does:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Subscriber Management | Checks who can use the network and lets only approved people in. |
Traffic Management | Makes sure voice and video data are clear by using Quality of Service (QoS). |
Fault Detection & Reporting | Watches for problems and tells staff fast to fix them quickly. |
Bandwidth Allocation | Shares internet speed fairly and changes it when needed. |
Forwarding Engine | Sends data between Ethernet and optical networks so it goes to the right place. |
Network Management Interface | Gives tools for staff to set up, watch, and control the OLT and network. |
Data Usage & SLA Tracking | Tracks how much data each user uses and checks if service rules are followed. |
The EPON OLT also does these things:
It controls how data moves to stop slowdowns.
It uses dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) to give users the speed they need.
It checks each user’s identity to keep things safe.
It has tools to watch the network and fix problems fast.
The EPON OLT keeps the network safe and steady. It makes sure all users get fair and good service.
The EPON OLT’s design helps it send and manage data well. The OLT connects to the main network on one side. On the other side, it connects to many ONUs through the optical distribution network (ODN).
Below is a simple diagram of how the EPON OLT is set up:
[Core Network] | [OLT] | [ODN - Splitters] | [ONU1] [ONU2] [ONU3] ... [ONUn]
The main parts of the EPON OLT setup are:
OLT (Optical Line Terminal): This device is at the provider’s office. It controls all data and gives time slots to each ONU.
ODN (Optical Distribution Network): This network uses splitters to send data from the OLT to many ONUs.
ONU (Optical Network Unit): These are at the user’s place. They change light signals into electrical signals for devices.
The EPON OLT uses smart features to work better:
Architectural Feature | Description |
|---|---|
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) | The OLT shares upload speed based on what ONUs ask for. This helps stop delays. |
Queue Scheduling Structure | The OLT uses queues to handle different data types like voice, video, and internet. |
Wavelength Multiplexing | The OLT sends many channels on one fiber, making data move faster. |
Wavelength/Channel Bonding | New EPON systems let ONUs use more than one channel. The OLT manages this to make uploads faster. |
Centralized Control | The OLT is the main boss. It manages speed, plans data, and keeps things organized. |
The OLT uses smart ways to share wavelengths and speed. It can give different ONUs what they need. This setup lets the EPON OLT help many users and give fast internet, even when lots of people are online.
The EPON OLT’s smart setup helps it handle lots of data. It keeps the network fast, fair, and steady for everyone.
GPON and EPON are both types of PON. They use OLT devices to connect users and manage the network. GPON follows ITU-T G.984 rules. EPON uses IEEE 802.3ah rules. GPON supports data, voice, and video. EPON mostly handles Ethernet data. GPON uses two layers for sending data. These layers are GEM and GTC frames. This lets GPON work with ATM and Ethernet traffic. EPON sends Ethernet frames in their normal format. This makes EPON simpler.
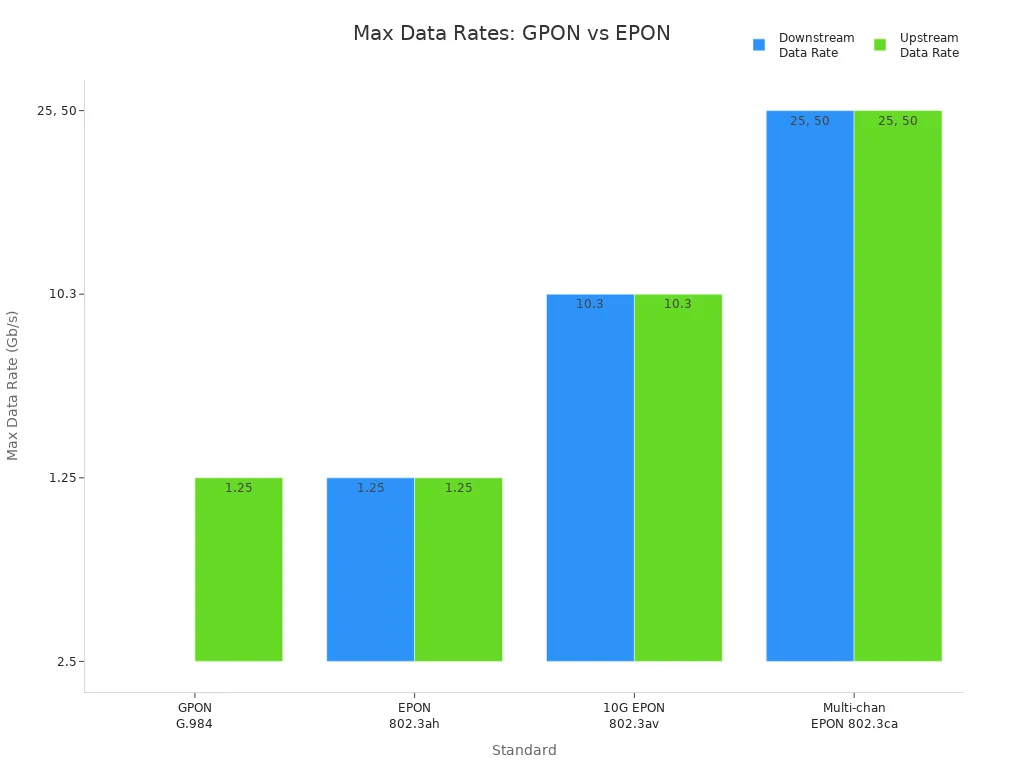
GPON gives higher download speeds. It can reach up to 2.5 Gb/s. EPON gives the same speed for download and upload. Both are 1.25 Gb/s. New EPON standards can go up to 10 Gb/s. Some can even reach 25 or 50 Gb/s. GPON can serve more users per OLT port. It can also cover longer distances. EPON is easier to manage. It costs less for data-only services.
Feature | GPON | EPON |
|---|---|---|
Protocol Standard | ITU-T G.984 | IEEE 802.3ah |
Service Types | Data, voice, video, IP services | Mainly Ethernet-based services |
Bandwidth | Up to 2.5 Gb/s downstream, 1.25 Gb/s upstream | 1.25 Gb/s symmetrical; up to 50 Gb/s in new standards |
Transmission Range | Up to 20 km | Up to 10 km |
Splitting Ratio | Up to 1:128 | Up to 1:64 |
Layering Complexity | Double encapsulation (GEM, GTC) | Native Ethernet frames |
GPON is used for home internet. Many telecom companies use it for FTTH and fiber access. GPON gives internet, phone, and TV with one fiber. It works well in places like hospitals, trains, and power companies. GPON can handle Ethernet and older TDM traffic.
EPON is good for modern IP services. It is often picked for business networks. EPON matches Ethernet rules, so it fits with old systems. EPON usually costs less. It is a smart choice for data-only needs. Where and how companies use these depends on their plans.
GPON: Used for FTTH, FTTx, mobile backhaul, and businesses.
EPON: Picked for business, modern data networks, and places with strong Ethernet.
Both use PON design, OLT devices, and splitters to connect many users.
Industry / Sector | GPON Usage Details |
|---|---|
Telecommunications | High bandwidth, FTTH, mobile backhaul, strong adoption in 4G/5G regions |
Healthcare | Used for secure and reliable connections |
Transportation | Supports smart infrastructure |
Energy & Utilities | Delivers stable network access |
Residential | FTTH and fiber access services |
Commercial Industries | Reliable and scalable broadband |
GPON is very important for fiber to the home networks. It connects homes to fast internet, phone, and TV with one fiber. The number of FTTH setups using GPON grew from 18% in 2020 to 29% in 2023. Now, GPON has about 60-65% of the market for these networks. This shows GPON helps many families get strong and quick internet all over the world.
GPON makes FTTH better by giving high speeds and good reliability. It can send data down at 2.5 Gbps and up at 1.25 Gbps. The network can reach homes up to 20 kilometers away. One central spot can serve many houses. Passive splitters help lower costs and make fixing easier. Governments and companies pick GPON for FTTH because it helps more people get online fast.
GPON Feature | Benefit for FTTH Users |
|---|---|
High Speed | Fast downloads and uploads for streaming, gaming |
Wide Coverage | Connects homes far from the central office |
Scalability | One OLT can serve many homes |
Low Maintenance | Fewer powered parts, less fixing needed |
Triple-Play Support | Internet, TV, and phone on one fiber |
GPON sends internet, phone, and TV over one fiber. This makes fiber-to-the-home networks easy and simple.
GPON also works for fiber-to-the-building setups. One fiber goes to a building and splits to serve many people inside. The system uses an OLT at the main office and ONTs at each customer’s place. Single-mode fiber and passive splitters can connect up to 128 users. GPON SFP transceivers work at 1490 nm for download and 1310 nm for upload. There are different types for longer distances.
GPON in FTTB setups gives up to 2.5 Gbps download speed, shared by users. Each person can get close to 1 Gbps, depending on how much they need. The network uses AES encryption to keep data safe. It uses TDMA to share bandwidth fairly. Where splitters are placed changes how well the network works and how easy it is to grow.
Component/Parameter | Specification/Role in FTTB |
|---|---|
OLT | Controls traffic, connects to core network |
ONT/ONU | Interfaces with user devices |
Splitters | Passive, splits signal to many users |
Max Users per PON | Up to 128 |
Max Reach | Up to 20 km |
Bandwidth | Up to 2.5 Gbps downstream |
GPON gives lots of bandwidth for internet, TV, and phone in FTTB. This makes it great for apartments, hotels, and offices.
Many companies use GPON to build strong and big networks. It gives gigabit-speed internet, supports lots of users, and saves money by using passive splitters. GPON helps businesses use cloud services, video calls, and HD streaming without problems. It can support up to 64 users per port and can upgrade to faster systems when needed.
GPON keeps data safe with strong encryption and blocks interference. Companies can use internet, phone, and TV over one fiber, making networks easy to set up. Central management lets staff watch and fix problems quickly. Businesses often use GPON with their IT systems by setting up OLTs, using VLANs, and remote monitoring tools. Combo PON lets upgrades happen without changing cables or devices.
GPON makes networks work better and grow easily.
It gives gigabit-speed internet for business needs.
The system lowers costs and helps future growth.
Security features keep data private and service steady.
Central management helps keep service good.
GPON helps smart cities and IoT by giving strong, fast connections for new business needs.
GPON OLT and EPON OLT are both important for passive optical networks. GPON gives faster speeds and can handle more users. This makes it good for big internet services. EPON is cheaper to set up and easy to upgrade. It works well for smaller networks. Both help networks get ready for new uses and more people.
GPON: More bandwidth, better quality, grows with more users
EPON: Works with Ethernet, costs less, easy to run
Picking the best PON technology helps networks stay strong, grow, and work well.
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Network.
It uses fiber cables to send data quickly.
One main device connects to many homes or businesses.
The system splits signals so many people can use the same line.
Speed Type | Maximum Speed |
|---|---|
Download | 2.5 Gbps |
Upload | 1.25 Gbps |
These speeds let users stream videos and play games without lag.
Users need an ONT or ONU box at home or work.
This box changes light signals to data for computers, phones, and TVs.
Some boxes have Wi-Fi and phone ports.
GPON uses strong encryption to protect data.
Each user gets a password and ID.
Fiber cables are hard to tap, so they keep information private.
Place | Use Case |
|---|---|
Homes | Fast internet, TV, phone |
Businesses | Reliable connections |
Apartments | Shared high-speed internet |
GPON works well in cities, towns, and rural areas.