Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-15 Origin: Site








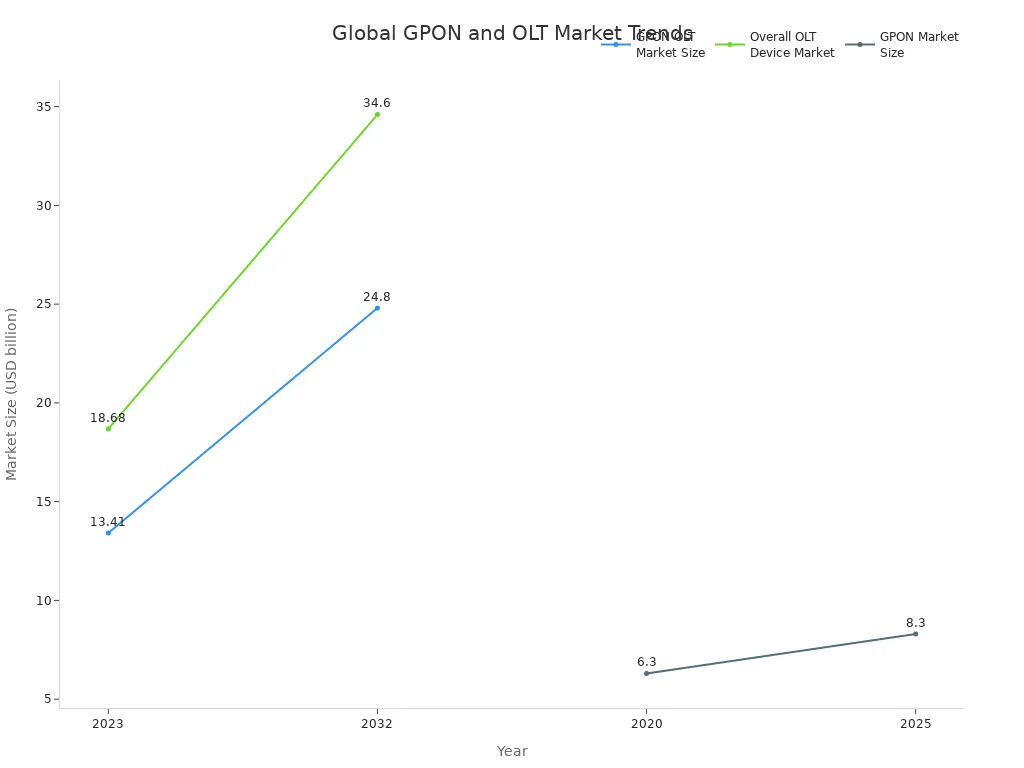
GPON ONU(ONT) is the device at your home. It changes optical signals into data. This data is used for internet, voice, and video. GPON OLT is at the provider’s office. It sends and manages data for many users. EPON OLT does similar work but uses Ethernet rules. It is often found in older networks. These devices help give fast internet connections. The GPON equipment market is growing quickly. People want faster speeds and smart cities.
GPON ONU(ONT) devices are found in homes or offices. They change optical signals into data. This data is used for internet, voice, and video services.
GPON OLT devices stay at the provider’s office. They control data, bandwidth, and security for many users. They help manage the network.
GPON and EPON use different technologies and rules. Their ONUs and OLTs cannot work together on one network.
The OLT and ONU work together to give fast and safe internet. They control how data moves and share fiber lines well.
Picking the right fiber technology helps providers give better broadband. It also makes services easy to grow and saves money for homes and businesses.
The GPON ONU, also called ONT, means Optical Network Unit or Optical Network Terminal. In a gigabit passive optical network, this device is at the user's place. It works as a gateway between the passive optical network and the user's equipment. International standards say ONU and ONT both end the PON and give service for data, voice, and video. The difference in names comes from history and standards groups. ITU-T uses ONT for single-user devices. IEEE uses ONU for devices that can help many users. Today, most technical papers use ONU and ONT for the same thing. Both change optical signals to electrical signals and connect users to the PON.
Tip: ONT and ONU mean the same thing in most fiber-to-the-home networks. The name might be different, but the job is the same.
GPON ONU(ONT) devices are put at the end user’s home or office. In a fiber-to-the-home setup, the ONU connects to the drop fiber part of the optical network. This part links the main optical point to the user’s box. The ONU is inside the house, often in a small box near the fiber entry. This spot lets the fiber reach homes, giving fast internet to everyone.
Network Component | Location | Role in PON Topology |
|---|---|---|
OLT | Central office | Manages and sends data to ONUs/ONTs |
Passive Splitter | Neighborhood cabinet | Splits signal to multiple ONUs/ONTs |
ONU/ONT | User premises | Converts optical to electrical signals |
Customer Devices | Home/office | Receives data from ONU/ONT |
In fiber to the house setups, ONTs are inside and connect to user devices like routers, phones, and computers. ONUs can also help buildings with many homes or outdoor cabinets, serving several users in one spot.
GPON ONU(ONT) devices do many important jobs in a PON network:
Signal Conversion
The ONU gets optical signals from the OLT and changes them to electrical signals for user devices. It also changes electrical signals from the user back to optical signals for sending upstream.
Service Delivery
ONUs give high-speed internet, voice, and IPTV. They let triple-play services work, so they are important for FTTH and fiber-to-the-home setups.
Data Aggregation and Optimization
The ONU gathers data from user devices, organizes it, and sends it upstream to the OLT. This keeps data moving smoothly and quickly.
Security and Management
Security features like firewalls and encryption keep user networks safe. ONUs also allow remote management, so providers can check and fix problems without going to the site.
Quality of Service (QoS)
ONUs give more bandwidth to important services like voice and video. This makes sure these services work well even when many people use the network.
Multi-Service Integration
ONUs have many ports, like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and voice ports. This helps many devices and services work in homes and businesses.
Note: ONUs and ONTs are very important for giving gigabit speeds and good service in modern passive optical networks.
How Data Moves Through the ONU/ONT:
The OLT sends one optical signal through the fiber.
A passive splitter divides the signal for many ONUs/ONTs.
The ONU gets the optical signal and changes it for user devices.
User devices send data back to the ONU.
The ONU changes this data to optical signals and sends it upstream to the OLT.
This way, many users can share one fiber easily. Gigabit passive optical network technology is great for homes and businesses.
EPON OLT means Ethernet Passive Optical Network Optical Line Terminal. This device is at the provider’s main office or data center. It works as the main server for the EPON system. The EPON OLT links the core Ethernet network to the passive optical network. It is the main spot for all subscriber connections. Each OLT has many virtual links. Each link connects to an ONU. These links keep user data safe and private. The OLT sends data using Ethernet frames. This makes it easy to use with current Ethernet networks. The device can send data in bursts. This helps control traffic from many users at once.
The EPON OLT follows IEEE 802.3ah rules. These rules tell how it manages data, controls bandwidth, and handles users.
EPON OLT does many important jobs in a PON network:
Changes electrical signals from the Ethernet network into fiber optic signals for the passive optical network.
Coordinates multiplexing between the OLT and ONUs. This lets many users share the same fiber.
Manages both upstream and downstream data flows. This keeps the network working well.
Collects traffic from all ONUs and sends it to the core network.
Handles user management, including checking who is allowed and service agreements.
Gives bandwidth using Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA). This gives users the speed they need when they need it.
Makes sure voice, video, and data services work well by enforcing Quality of Service (QoS).
Watches the network and does maintenance to keep it reliable.
The OLT also uses the OMCI protocol. This helps set up and manage ONUs, including updating software and checking status.
EPON is important in modern fiber optic networks, especially in cities. EPON OLT helps give fast internet to homes, offices, and buildings. EPON works in many ways, like Fiber to the Building (FTTB) and Fiber to the Desktop (FTTD). This technology uses passive optical splitters. This lowers building and upkeep costs. EPON gives equal speeds up to 1.25 Gbps and can upgrade to 10 Gbps. The system works well with current Ethernet networks. This makes upgrades easy and saves money.
Aspect | EPON OLT | GPON OLT |
|---|---|---|
Protocol | Ethernet-based packet transmission | Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) |
Data Rates | Symmetrical (1.25 Gbps up/down) | Asymmetrical (2.5 Gbps down, 1.25 Gbps up) |
Frame Type | Variable-length Ethernet frames | Fixed-length cells |
Architecture | Simple, Ethernet-centric | Complex, multiprotocol |
Integration | Easy with Ethernet networks | Needs more conversions |
Cost | More cost-effective | Higher due to complexity |
EPON OLT systems use Ethernet rules, so they fit well in current networks. This makes EPON flexible and easy to grow for city broadband. EPON OLT types can be different in port count, speed, and features. Providers can pick what works best for them. Compared to gigabit passive optical network systems, EPON is simpler and saves money for many operators.
The GPON OLT is very important in the network. It stays at the provider’s main office. It links the core network to homes and businesses. The OLT uses lasers to send signals through splitters. These signals can reach up to 128 ONUs or ONTs. The farthest distance between the OLT and users is 16 kilometers. This helps keep service good.
GPON OLT hardware has many parts:
PON ports let many ONUs connect and support fast speeds.
GPON OLT SFP modules help send data between the OLT and ONUs. They make upgrades easy and work with different brands.
Redundant power supplies keep the network working if one power fails.
Modular design lets providers add or change parts without stopping service.
Software features help run and protect the network:
Management tools watch performance, fix problems, and track devices.
Security systems use authentication, access control, and encryption to keep data safe.
Quality of Service (QoS) makes sure voice and video work well.
Troubleshooting protocols help find and fix network issues.
GPON OLT follows ITU-T G.984 rules. It changes Ethernet frames into optical signals and sets bandwidth limits. Downstream speeds can be up to 2.5 Gbps. Upstream speeds can be up to 1.25 Gbps. The OLT uses special protocols for error correction and encryption. This keeps data safe and correct.
The OLT is the main controller in the PON system. It manages connections and data between the core network and ONUs.
The OLT is the center of the GPON network. It links the core network to the optical distribution network. The OLT manages both upstream and downstream data. It makes sure each user gets enough bandwidth. The OLT uses Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) to change bandwidth for each ONU as needed. This keeps internet services working well, even when many people are online.
The OLT also keeps the network safe. It uses authentication and encryption to protect user data. The device checks how the network is working. It watches for delays and makes sure data moves correctly. It plans when data is sent and makes sure each ONU gets the right data. The OLT works with billing systems to track usage and control access.
GPON OLT supports a tree layout. It uses passive optical splitters to reach many users. It uses single-fiber bi-directional transmission with Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). This separates upstream and downstream signals. This setup helps send broadband services to homes and businesses easily.
GPON OLT Role | Description |
|---|---|
Central Hub | Connects core network to optical distribution network |
Bandwidth Management | Allocates bandwidth using DBA |
Security Enforcement | Uses authentication and encryption |
Performance Monitoring | Checks latency, throughput, and system health |
Service Provisioning | Activates and manages broadband services |
Fault Detection | Identifies and isolates network problems |
GPON OLT does many jobs to keep the network fast and safe:
Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) lets the OLT set up ONT devices automatically. This lowers mistakes and saves time.
Multi-vendor Support means it works with ONUs and ONTs from different brands.
Service Eligibility Checks let the OLT check for signal problems before turning on services.
Centralized Management helps providers watch devices, find faults, and make reports.
Automated Service Provisioning lets the OLT set VLANs, QoS rules, and turn services on or off.
Security Functions use authentication, access control, and encryption to keep data safe.
Quality of Service (QoS) makes sure voice and video calls stay clear, even when the network is busy.
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) lets the OLT change bandwidth for each user as needed.
Network Monitoring helps the OLT check ONT status, watch alarms, and test signals to find problems early.
Redundancy and Reliability means backup power and links keep the network working during failures.
Compliance and Scalability means the OLT follows world standards and can grow as more users join.
Tip: Updating software and checking equipment often helps the OLT work well and avoid problems.
GPON OLT uses advanced protocols like OMCI for line control and authentication. It puts Ethernet packets into GEM ports, TCONT queues, and VLAN IDs. These features help the OLT give internet, voice, and video with high speed and reliability.
ONU and OLT talk to each other in a set order. This helps all devices work together well. Here is what happens:
The OLT sends Ethernet data to all ONUs at once.
It starts ranging to match ONUs’ timing and saves their times.
The OLT gives each ONU a time and amount to send data.
The ONU changes optical signals to electrical signals for users and collects data to send back.
The ONU sends data in short bursts, and the OLT controls this to stop crashes.
When setting up, the OLT finds new ONUs, checks who they are, and gives them an ID. The OLT and ONU measure delay and match data timing. This keeps the network safe and steady.
Note: This careful process lets many people use one fiber without problems.
Data flow in GPON starts at the OLT, which links to the main network. The OLT turns digital signals into optical signals and sends them through fiber. A passive splitter breaks the signal so many ONUs or ONTs can get it. Each ONU at a home or business turns the optical signal back into electrical signals for things like computers and phones.
The OLT controls both downstream and upstream data. Downstream data goes from the OLT to all ONUs at the same time. Upstream data moves from each ONU to the OLT in short bursts, using a schedule from the OLT. This uses time slots to stop data crashes and keeps the network working well.
Here is a table with the main steps in data flow:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
1. OLT Conversion | OLT turns digital signals into optical signals |
2. Signal Splitting | Passive splitter breaks signal for many ONUs |
3. ONU Conversion | ONU turns optical signals into electrical signals |
4. Upstream Burst | ONU sends data in bursts, OLT controls timing |
This setup helps FTTH networks give strong broadband to homes and businesses.
ONU and OLT working together give users many good things. People get fast internet for streaming, gaming, and browsing. The system supports FTTH, so fiber can go right to homes and offices. The OLT can help many users at once, so the network can grow.
Users get steady broadband because the OLT has backup and strong power. The ONU uses little energy and fits in any home or business. Security keeps user data safe, and the OLT manages quality so voice and video stay clear.
Tip: ONUs have ports for Ethernet, phone, and TV, so they work with many devices.
The network can reach up to 20 kilometers and give fast speeds, meeting today’s needs.
GPON ONU(ONT) and GPON OLT work as a team to give fast fiber internet. The ONU or ONT is at your home or office. It changes optical signals into data for your devices. The OLT is at the provider’s office. It controls data, bandwidth, and keeps things safe for many users. EPON OLT does almost the same jobs. It can handle both IP and TDM services. These devices help homes, businesses, and cities get strong and quick internet.
Device | Main Role | Benefit for Users and Providers |
|---|---|---|
GPON ONU/ONT | Converts optical signals for end-user devices | Fast, stable internet at home or office |
GPON OLT | Central control and bandwidth management | Reliable, scalable, secure network |
EPON OLT | Aggregates and manages EPON network traffic | Flexible, cost-effective broadband |
Picking the best fiber technology helps networks work better, stay safe, and grow in the future.
GPON ONU(ONT) sits at the user’s home or office. It changes optical signals into data for devices. GPON OLT stays at the provider’s office. It manages and sends data to many ONUs or ONTs.
Yes. One GPON OLT can connect to up to 128 ONUs or ONTs through splitters. This setup helps providers serve many homes or businesses using a single fiber line.
Yes. GPON ONU(ONT) needs electrical power at the user’s location. It uses this power to change optical signals into data for devices like computers, phones, and TVs.
GPON OLT uses encryption and authentication. These features protect user data from outside threats. The OLT checks each ONU(ONT) before allowing access to the network.
No. GPON ONU(ONT) and EPON ONU use different protocols. They cannot work on the same network. Providers must match the ONU type with the correct OLT for proper service.