Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-20 Origin: Site








GPON means Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It gives fast internet, voice, and video using one fiber. Many groups pick GPON because it works well and can grow in the future. Picking the best fiber optic technology affects cost, network strength, and service quality.
The main reasons groups pick GPON are:
Lower setup and running costs because of passive splitters and no powered gear in the network.
Better bandwidth and longer reach than copper.
Easy to add new users with few changes.
More reliable and fewer things can break.
Can support many services on one fiber, so it is easier to manage for both providers and users.
Olt devices help control these networks. EPON OLT gives similar benefits but is different in some technical ways.
GPON gives fast and steady internet, voice, and video on one fiber. This makes it cheaper and simple to grow the network. GPON uses passive splitters that do not need power. This lowers upkeep and makes the network more stable. GPON has faster speeds and better service than EPON. It also has strong security and can control bandwidth well. GPON is good for homes and businesses that need many services. EPON works better for Ethernet networks and easy setups. Future GPON upgrades will give even faster speeds. They will help smart city and IoT tech, so the network can grow for a long time.
GPON means Gigabit Passive Optical Network. It is a kind of network that uses fiber to give fast internet, voice, and video to homes and businesses. GPON uses optical splitters to let many people share one fiber. This makes it cheaper for big networks. The network has three main parts: the Optical Line Terminal (OLT), optical splitters, and Optical Network Terminals (ONTs) or Optical Network Units (ONUs). The OLT is at the provider’s office and controls data and the network. GPON can connect one fiber to many people. It does not need powered equipment outside. This makes the network work better and need less fixing.
GPON lets providers give voice, video, and internet on one fiber. It also keeps data safe with strong encryption.
GPON is special because it has smart features and can be used in many ways. Here are some important things about it:
Uses Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) for different upstream and downstream signals.
Gives more bandwidth: up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream, which is more than EPON.
Uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) to share bandwidth for each person.
Can split one fiber for 16 to 64 users.
Works for up to 20 km, so it is good for cities and country areas.
Uses passive optical splitters that do not need power, so the network is more reliable.
Has strong encryption and VLAN support for privacy and safety.
Gives voice, video, and internet and works with many protocols like Ethernet, IP, video, and VoIP.
Feature | GPON Specification |
|---|---|
Downstream Data Rate | Up to 2.5 Gbps |
Upstream Data Rate | Up to 1.25 Gbps |
Max Split Ratio | 1:64 |
Max Distance | 20 km (typical), up to 60 km max |
Key Components | OLT, ONT/ONU, optical splitters |
Supported Services | Voice, video, internet |
GPON is easy to grow and saves energy. It is a top pick for new broadband networks. It lowers costs by letting many people use one fiber. It also needs fewer powered devices outside.
GPON moves data from the main office to homes and businesses in a smart way. The OLT begins by sending light signals through fiber cables. These cables work like highways for light. They move information fast and keep it safe. The light reaches passive optical splitters. The splitters break the light into many paths. Each path goes to an ONU at a user’s place.
The OLT sends the first light signal.
Optical fibers move the signal far.
Passive optical splitters share the signal with many users.
Each ONU gets the signal and turns it into electricity for devices.
To send data back, ONUs change electricity into light again.
GPON uses parts that do not need power outside. This makes the network strong and simple to run. Security tools like encryption and QoS keep data safe and help important traffic move well. The OLT decides how much bandwidth each user gets. This keeps data sharing fair for all.
GPON networks use a point-to-multipoint setup. One OLT at the main office links to many users with one fiber. Passive optical splitters let one OLT port serve up to 64 users. The splitters can be at the main office or closer to users. This depends on how many people need service nearby.
In cities, splitters are often at the main office. This helps internet providers control the network better. In suburbs or places with fewer people, splitters may be put in a row to reach more homes. The network has three main parts: the OLT, the ODN with fibers and splitters, and the ONUs at each user’s place.
Component | Function |
|---|---|
OLT | Starts and manages data transfer |
Optical Splitter | Divides optical signals for many users |
ONU | Changes optical signals for user devices |
This setup lets GPON give fast and steady data to many users. It also keeps costs low and makes the network easy to grow.
An EPON OLT sits in the middle of the network. It is the main controller for data between the provider and users. The OLT links to many ONUs or ONTs using optical splitters. It controls how data moves and keeps the network safe. It also makes sure users get enough bandwidth. There are different OLT types for different network sizes. Some OLTs work for small networks. Others can handle thousands of users.
The main jobs of an EPON OLT are:
Managing users so only allowed people connect
Keeping data moving without problems
Finding and reporting problems fast
Giving bandwidth based on what users need
Watching and setting up the network easily
EPON OLTs let providers give fast internet, voice, and video to many people at once.
EPON uses Ethernet rules over fiber for fast and steady connections. It can give the same or different speeds for upload and download. This makes it good for many needs. Optical splitters let one OLT connect to many ONUs. This setup saves money and is easy to make bigger.
Technical Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Definition | Ethernet Passive Optical Network using Ethernet protocol and passive optical parts |
Bandwidth Allocation | Same or different speeds, up to 1.25 Gbps total |
Encryption | Uses AES to keep data safe |
Network Components | OLT, ONUs/ONTs, optical splitters, optical fiber |
Upstream Data Transmission | Uses TDMA so everyone shares fairly |
Standards | Follows IEEE 802.3ah |
Topology | Point-to-multipoint |
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation | OLT gives bandwidth as needed |
VLAN Tagging | Supports IEEE 802.1Q |
Scalability and Reliability | Can grow big and works well |
Energy Efficiency | Uses less power than active networks |
EPON lets the OLT control traffic, give out bandwidth, and keep data safe. It gives fast data to many users without slowing down.
OLT EPON is important for both providers and users. Providers get a cheap way to give fast internet. One OLT can serve many people, so the network can grow easily. EPON OLTs use Ethernet rules, so they fit with old systems and are easy to manage.
Key benefits for providers:
High speeds and low wait times for smooth internet and video
Can serve many people at once, good for busy places
Quality of Service helps voice and video work better
Strong safety with user checks and encryption
Easy to control the whole network from one place
Users also get big benefits:
Fast and steady internet with little delay
Enough speed for many devices and smart homes
Good service in cities and far away places
Easy to upgrade as more people join
OLT EPON gives better speed, trust, and lower costs for all. EPON OLTs help more people get online and support future needs.
GPON and EPON follow different rules and standards. GPON uses the ITU-T G.984 standard. EPON uses IEEE 802.3ah. GPON gives faster speeds and better service control. EPON uses Ethernet frames, so it fits old networks easily. Both use point-to-multipoint setups, but their layers and how well they work are not the same.
Feature | GPON | EPON |
|---|---|---|
Protocol Standard | ITU-T G.984 | IEEE 802.3ah |
Speed (Down/Up) | 2.5 Gbps / 1.25 Gbps | 1 Gbps / 1 Gbps |
Efficiency | Higher bandwidth efficiency | Simplified Ethernet support |
Deployment Cost | Higher due to complex tech | Lower due to Ethernet base |
Integration | Requires protocol adaptation | Ethernet-native |
GPON uses ATM and TDM to send data. It supports many services and strong QoS. EPON uses Ethernet frames with small changes. This makes EPON cheap and easy to set up where Ethernet is used. GPON is good for phone companies needing many services and strong QoS. EPON works well for places that use lots of IP traffic and want cheaper broadband.
Layer | GPON | EPON |
|---|---|---|
Network (L3) | ATM, TDM, IP | TDM, IP |
Data Link (L2) | Ethernet, GFP | Ethernet with MPCP |
Physical (L1) | PON-PHY | PON-PHY |
GPON and EPON are different in how they share bandwidth, work, and stay reliable. GPON gives different speeds for download and upload. It can go up to 2.5 Gbps down and 1.25 Gbps up. EPON gives the same speed for both, usually 1 Gbps. GPON uses DBA and five T-CONT types to pick which traffic is most important. EPON uses the MPCP rule for sharing bandwidth but does not sort traffic by importance.
Feature | GPON | EPON |
|---|---|---|
Bandwidth Rates | Asymmetric: 2.5Gbps down, 1.25Gbps up | Symmetrical: 1Gbps down/up |
Bandwidth Allocation Method | DBA with multiple T-CONT types for QoS | MPCP protocol, no service priority classification |
QoS Support | Differentiated QoS, five T-CONT types | No service priority, random bandwidth competition |
Efficiency | High, flexible rates, advanced DBA | Lower, fixed rates, lacks advanced QoS |
Multi-service Support | Supports ATM, GFP, better OAM management | Simpler, cost-effective, lacks advanced multi-service support |
GPON is very efficient and has strong QoS. This makes it good for places needing many services. EPON has lower delay, which helps games and video calls. GPON has been used for a long time and is very stable. EPON is newer and sometimes has trouble working with other systems. EPON’s same upload and download speeds help when sending lots of data. GPON’s slower upload can make some things slower.
Aspect | EPON | GPON |
|---|---|---|
Latency | Lower latency, good for real-time apps | Higher latency, due to asymmetrical bandwidth |
Reliability | Newer, some interoperability issues | Mature, stable, proven reliability |
Bandwidth | 10 Gbps symmetrical possible | 2.5 Gbps down, 1.25 Gbps up |
Scalability | More scalable, Ethernet foundation | Limited scalability for future growth |
Upstream Performance | Suited for upstream-heavy traffic | Slower upstream speeds |
GPON and EPON are used in different ways. GPON is best for homes and regular internet. It is cheap for big groups and gives many services without needing VLANs. EPON is better for businesses and places with lots of Ethernet. It lets you control things closely with VLANs and fits business needs.
Feature/Aspect | GPON | EPON |
|---|---|---|
Typical Deployment | Residential and general broadband | Business environments |
Bandwidth | 2.5 Gbps downstream, 1.25 Gbps upstream | Symmetrical 1 Gbps downstream/upstream |
Network Complexity | Simpler, no VLANs required | More complex, requires multiple VLANs |
Service Segmentation | Less granular, broad services | Granular control via VLANs |
Cost-effectiveness | Cost-effective for large-scale residential | Higher complexity, better for Ethernet-based business |
Scalability | High, wide range of services | Suitable for Ethernet segmentation and business needs |
EPON is used more in Asian countries like Japan, China, Korea, and Taiwan. It works well with IP traffic and makes network jobs easier. EPON gear costs less, so it is good for saving money. EPON uses one Layer 2 network, which lowers extra work and cost. GPON is mostly used in North America and Europe. Phone companies there need strong service control and trust.
Tip: Service providers should think about network size, needed speed, and what they already have before picking GPON or EPON. Choosing the right OLT is important for how well the network works and grows.
GPON needs regular checks of OLT and ONU devices. Providers must look at system logs and check the fiber network. They also need to keep network tools and outdoor gear working. EPON is easier to take care of because it uses Ethernet and one management system.
GPON gives homes fast and steady internet. Providers use it for internet, TV, and phone on one fiber. Families can stream shows, play games, and use smart devices easily. GPON SFP modules help connect homes to fast internet and Ethernet.
GPON lets you use internet, TV, and VoIP together.
Many devices can work at once without slowing down.
Providers add new users quickly and easily.
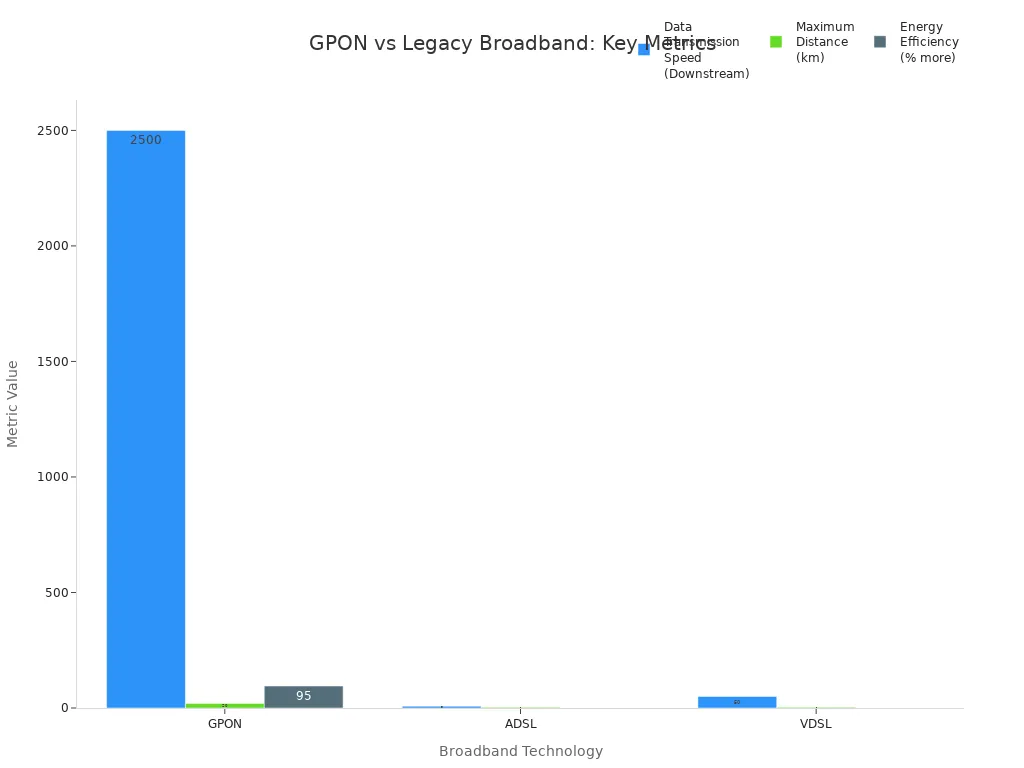
GPON works better than older broadband types. The table below shows how GPON compares to ADSL, VDSL, and DOCSIS:
Feature | GPON (Fiber Optic) | ADSL (Copper) | VDSL (Copper) | DOCSIS (Coaxial Cable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Data Transmission Speed | Up to 2.5 Gbps down, 1.25 Gbps up | Up to 8 Mbps | Up to 50 Mbps | High-speed, limited by cable |
Maximum Distance | Up to 20 km | Up to 3 km | Up to 3 km | Limited by cable length |
Equipment Requirements | Less equipment needed | More equipment needed | More equipment needed | Uses existing cable |
Energy Efficiency | 95% more efficient | Less efficient | Less efficient | N/A |
Stability | Stable, immune to interference | Less stable | Less stable | N/A |
Service Flexibility | Supports many services | Limited flexibility | Limited flexibility | Limited flexibility |
Businesses need internet that is fast, safe, and easy to grow. GPON gives high speeds and smart features. It keeps voice, video, and data separate for better quality. GPON can connect up to 128 users to one optical line terminal. This is good for offices, hotels, and schools.
Advantage Aspect | GPON Features and Benefits | EPON Comparison / Notes |
|---|---|---|
Bandwidth | Up to 2.5 Gbps down, 1.25 Gbps up, supports business needs | Typically 1 Gbps symmetric speeds |
Reach | Up to 20 km, fits urban and rural sites | Shorter reach |
Splitter Ratios / Scalability | High splitter ratios, more users per fiber | Lower splitter ratios |
Quality of Service (QoS) | Advanced QoS, custom bandwidth for services | Less flexible QoS |
Network Layer Separation | Separates data types for better quality | Combines all data types |
OAM | Advanced monitoring and management | Less advanced |
GPON uses encryption like AES to keep data private. VLANs split the network to make it safer. Providers can add new users to splitters, saving time and money. Fiber optic lines do not get interference, so connections stay strong.
Providers can watch and fix problems quickly.
Businesses can grow without changing the main network.
GPON connects many users over big areas and saves money.
GPON and EPON will keep getting better as more people want fast internet. The passive optical network market may reach $37.1 billion by 2030. GPON leads because it is fast and easy to grow. People want HD video, cloud apps, and online games, so networks must improve.
New GPON types like XG-PON, XGS-PON, and NG-PON2 will be even faster. These upgrades let providers serve more users without new fiber. Networks will support both fixed and mobile services, smart cities, and IoT.
Emerging Technology | Key Features and Impact |
|---|---|
10G-PON (XGS-PON, 10G-EPON) | 10 Gbps speeds, supports 4K/8K streaming, cloud, IoT, coexists with GPON, energy efficient |
NG-PON2 | Higher speeds, smooth upgrades |
25G/50G EPON | Meets enterprise needs, easy upgrades |
Market Impact | Expands subscribers, lowers costs, ensures future-ready connectivity |
NG-PON2 will give more speed and space for future needs.
GPON will help with 5G, IoT, and smart city projects.
Providers can grow broadband without big changes to their networks.
GPON is special because it gives more bandwidth, better security, and strong reliability. The table below shows how GPON and EPON are different:
Feature | GPON Advantages | EPON Limitations |
|---|---|---|
Bandwidth | Up to 2.5 Gbps down, 1.25 up | 1 Gbps symmetrical |
Security | Strong encryption | Less emphasis |
Scalability | Large-scale, long distance | More limited |
Groups should think about these things:
Figure out how much bandwidth is needed.
Make sure devices work with the network.
Get ready for more users in the future.
Check if everything meets the right standards.
Good planning helps pick the best fiber optic network for every need. For extra help, look at technical guides about GPON and EPON networks.
GPON uses ITU-T rules and has faster downloads. EPON uses IEEE rules and works with Ethernet frames. GPON is good for many types of services. EPON is best for networks that already use Ethernet. Both use fiber optic cables to send data quickly.
An OLT controls data between the provider and users. It sends signals through fiber cables. It manages bandwidth and keeps the network safe. The OLT links to many ONUs with splitters.
GPON gives fast internet, TV, and phone on one fiber. It lets many devices work at the same time. It uses less power and needs fewer devices. Families get strong connections for streaming, gaming, and smart gadgets.
Yes, people ask about setup, speed, and how it works. They want to know how OLT EPON helps many users and keeps data safe. Providers explain how it fits with Ethernet networks.
GPON gives better service and supports more users per fiber. EPON is good for businesses that use Ethernet. The table below shows a quick comparison:
Feature | GPON | EPON |
|---|---|---|
Speed | Up to 2.5 Gbps | Up to 1 Gbps |
Scalability | High | Moderate |
QoS | Advanced | Basic |