Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-25 Origin: Site








GPON means Gigabit Passive Optical Network. OLT is an Optical Line Terminal. It is the main control in fiber networks. ONU and ONT are devices for users. They change optical signals to electrical signals. ONT is usually inside one home. ONU can help many users. The table below shows what each device does:
Device | Location | Main Function | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|---|---|
OLT | Central office | Manages everything, brings services together | Changes signals, controls traffic, gives out bandwidth |
ONU | Near user homes | Gives service to many users | Changes signals, sends data, links to different cables |
ONT | Inside user home | Works for one user | Changes signals for devices, gives voice, video, data |
Knowing about these devices helps people set up networks well. EPON OLT technology links millions of people. It helps fiber broadband grow fast.
OLT runs the fiber network from a main office. It handles data and internet speed for lots of people.
ONU helps many people in one area. It changes light signals to electric signals. ONT connects inside a house or office for just one person.
EPON OLT uses time sharing and splits internet speed. This lets many people get fast internet in a fair way.
Huawei ONT devices give quick and steady internet. They have strong Wi-Fi and are simple to set up. Smart tools make using them better and stop many problems.
Picking the best device and putting it in the right spot keeps fiber networks quick, safe, and steady for homes and businesses.
An OLT is very important in a PON network. It is found in the central office of the service provider. The OLT links the main network to many users using a passive optical network. It sends data to ONUs and ONTs, which are closer to people’s homes. OLT equipment is the main part of modern fiber broadband. OLT installation rules help it work well in many places. Service providers pick OLTs because they are reliable and can handle lots of data.
The OLT is the main controller in a PON network. It manages all the data between the provider and users. The OLT sends data to every ONU and ONT. Each ONU or ONT only reads its own data. The OLT organizes data from users with time division multiplexing. This stops data from crashing together and keeps things smooth. The OLT uses different light waves for sending and getting data. It uses 1490nm for sending and 1310nm for getting data. The OLT also shares bandwidth with dynamic bandwidth allocation. This lets all users get a fair share of bandwidth. OLT equipment helps millions of people use big networks.
Note: OLTs must be installed by following strict rules to keep them safe and stable.
Many service providers use OLTs with 16 ports. These OLTs help networks grow when more people join. They can send many data streams and make the network better. OLTs have strong security like encryption and safe logins. Easy management tools help people install and use OLTs. OLTs work with old equipment, so upgrades cost less. Extra features like load balancing and fixing errors make OLTs more reliable and lower downtime.
Some top OLT brands in the world are:
Huawei, famous for fast and new ideas in big FTTH networks.
ZTE, known for flexible and low-cost OLTs.
FiberHome, gives good local help and strong security.
Nokia, trusted for being stable and meeting world standards.
Calix, focuses on smart management and better bandwidth.
The OLT does many important jobs in a PON network. These jobs help control data, users, and network quality. The table below lists the main jobs of OLT equipment and what they do:
Function | Description |
|---|---|
Subscriber Management | Checks and allows users. Watches data use and follows service rules. |
Traffic Management | Makes sure voice and video get sent first. Gives them higher priority over other data. |
Bandwidth Allocation | Shares bandwidth among users. Stops one user from taking too much. |
QoS Engine | Follows quality rules. Handles different data types with the right priority. |
Forwarding Engine | Sends data between Ethernet and optical networks. Makes sure packets go to the right place. |
Network Management Interface | Gives tools to set up, watch, and control the OLT and network. |
The OLT connects to many ONUs and ONTs through the passive optical network. It handles both sending and getting data. The OLT makes sure each user gets enough bandwidth. It also keeps the network safe and working well. OLT equipment helps add new services and lets networks grow. OLT installation rules help set up the OLT safely and easily. OLT technology lets providers give fast internet, voice, and video to millions of homes.
An EPON OLT is found in the center of a fiber optic network. This device links the main network to the optical distribution network. The EPON OLT has many important parts. Each part helps the network work well.
The control board is like the brain. It runs all the device’s jobs.
DC power supply boards give steady power. If one fails, the other keeps the OLT working.
Fan units keep the device cool. They also check the air inside the subrack.
The subrack holds all the boards. It gives the OLT a strong frame.
Uplink boards link to the main network. These boards use GE or 10GE optical interfaces to connect to BRAS or other equipment.
Downlink (PON) boards have many PON ports. Each port links to ONUs or ONTs using passive optical splitters.
The EPON OLT structure lets data move fast. It helps providers give good internet, voice, and video to homes and businesses.
The EPON OLT follows steps to manage data and users. These steps help control how data moves up and down.
The OLT gets data from the main network. It gets this data ready for ONUs and ONTs.
The OLT sends data down to all ONUs and ONTs. Each endpoint picks out its own data.
The OLT uses optical splitters to share the signal. One OLT port can serve many ONUs or ONTs.
The OLT manages data going up with TDMA. It gives each ONU or ONT a time slot.
The OLT uses DBA algorithms. These change upstream bandwidth when traffic changes.
The OLT knows each ONU by its LLID. It sends grant messages to tell when each ONU can send data.
The OLT uses IEEE 802.3ah OAM and MPCP protocols. These help set up, fix problems, and watch performance.
This way, everyone shares the channel fairly. The EPON OLT can support up to 64 ONUs for each PON port. This makes it great for homes and small businesses.
Network Type | Maximum ONUs Supported per OLT PON Port | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
EPON | 64 ONUs (1:64 split ratio) | Residential, SME |
GPON | 128 ONUs (theoretical), commonly 64 | Mixed-use, Enterprise |
The EPON OLT controls data flow in a point-to-multipoint setup. This lets one OLT serve many ONUs and ONTs. The OLT sends Ethernet traffic to all endpoints. Optical splitters share the signal with many ONUs and ONTs. Each endpoint only gets its own data.
Data going up moves from ONUs and ONTs to the OLT. The OLT uses TDMA to control this flow. It sets time slots for each endpoint. The OLT uses DBA to change bandwidth when traffic changes. Each ONU has its own LLID. The OLT sends grant messages to say when each ONU can send data.
The OLT uses optical fibers to link to ONUs and ONTs. This setup gives fast and smooth data transmission. The EPON OLT can support millions of users in big networks. Providers use this technology for strong and flexible service.
Tip: The point-to-multipoint setup of EPON OLTs is great for fast service in growing areas.
ONU means Optical Network Unit. It is found at the edge of a fiber network. The ONU links the GPON system to user devices. It gets optical signals from the OLT. The ONU changes these signals into electrical ones. These go to computers, phones, or routers. The ONU also sends data back to the OLT. It turns electrical signals into optical signals for this. This lets users get internet, voice, and video.
The ONU has many features:
It is the end point at the subscriber’s place.
It changes optical signals from the OLT for devices.
It shares data using Ethernet ports or Wi-Fi.
It gives fast internet, voice calls, and IPTV.
It has optical receivers and converters inside.
It offers security like firewalls and encryption.
It supports Quality of Service for voice and video.
It allows remote management and fixing problems.
Some have built-in Wi-Fi and VoIP.
The ONU is often outside or in shared areas. It can serve many people in business parks or apartments. This helps providers reach more people with one device.
ONT stands for Optical Network Terminal. It is found inside homes or small offices. The ONT connects right to the fiber cable from the OLT. It changes optical signals into electrical ones for computers, phones, and TVs. The ONT also sends data back to the OLT. This lets users send and get data.
The ONT gives many services:
Internet through Ethernet ports or Wi-Fi.
Voice calls with VoIP or phone lines.
IPTV and video streaming.
Bandwidth control for each user.
Local management with web or command-line tools.
Security like encryption and user authentication.
Port Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
PON Port | Connects to the optical network |
Ethernet Ports | Connects to computers and routers |
Telephone Ports | Connects to phones |
Wi-Fi | Provides wireless access |
Video Ports | Connects to TVs or set-top boxes |
The ONT gives each home or office its own fiber link. This makes services fast and reliable.
ONU and ONT both connect users to the GPON network. They do many of the same things, but are used in different places.
ONU is usually outside or in shared spaces like utility rooms or rooftops.
ONU serves many people in business parks, campuses, or apartments.
ONT is inside a home or small business.
ONT gives a fiber link to one user or family.
ONU collects data from several users and sends it to the OLT.
ONT is the last point between the network and user devices.
Both can give high data rates, up to 10 Gbps.
Both support GPON, EPON, XG-PON, and XGS-PON.
The main difference is where they are and how many people they serve.
Note: ONU is the IEEE term. ONT is the ITU-T term. Both mean similar devices in fiber networks.
OLT, ONU, and ONT all have special jobs in a PON network. OLT is at the central office. It is the main controller for the fiber system. OLT manages data traffic and user connections. It also checks service quality. ONU and ONT work near users. They change optical signals from OLT into electrical signals. These signals go to computers and phones.
OLT controls the whole network. It watches devices and manages bandwidth. OLT sets up services for users. ONU and ONT do not control the network. They only change signals and send data to users.
Here is a table that shows how they manage networks:
Device | Network Management Capabilities |
|---|---|
OLT | Central office device; multi-service platform; centralized network management including device and port monitoring, service provisioning, user status monitoring, bandwidth allocation per QoS/SLA; controls ranging and bandwidth allocation for ONUs. |
ONU/ONT | Converts optical signals to electrical signals; aggregates and grooms data for upstream transmission; connected to end users; no centralized network management functions; ONT is the ITU-T term, ONU is IEEE term, both refer to user-side equipment. |
OLT can help many ONUs and ONTs at the same time. It uses PON technology to split signals. This lets it reach many homes or businesses. ONU is often outside or in shared places. ONT is usually inside one home or office. Both connect to OLT with optical fibers.
Tip: OLT controls the network. ONU and ONT connect users to the network.
OLT, ONU, and ONT work in many types of networks. OLT is best for big fiber networks. Internet providers use OLT to help thousands of users. OLT also helps smart cities and campus networks.
ONU and ONT help end users. ONT is often found in homes. It gives internet, IPTV, and phone service. ONU can help many people in apartments or business parks. Both devices give fast and steady fiber access.
The table below shows common ways each device is used:
Device | Common Use Cases in Residential Networks | Common Use Cases in Business Networks |
|---|---|---|
ONT (ONU) | - Installed at homes to convert optical signals to electrical signals | - Installed at business premises |
OLT | - Located at central office or network hub | - Core device in enterprise and campus networks |
OLT, ONU, and ONT work together to make PON networks strong. They help bring fast internet to homes, businesses, and cities.
Huawei ONT devices are special in fiber networks. They use new technology and are easy to use. Some models, like EG8145X6, have Wi-Fi 6. This means faster internet and better coverage. Homes and businesses get strong connections. Quality of Service keeps calls clear, even when many people use the network. Gigabit Ethernet ports give fast and steady links for computers and TVs.
Huawei ONTs work with other brands. This makes them good for many setups. They support IPTV and VoIP. They can also connect with ZTE GPON systems. Network tools help operators watch and fix problems quickly. Smart Wi-Fi features, like app analysis, make things better for users. These features also lower the number of service calls.
Huawei’s Trouble-Free ONT has a special 7dBi antenna. It uses smart Wi-Fi tools to make internet faster and stronger. This helps in homes with thick walls or many floors.
New models use the latest technology. The table below lists some popular Huawei ONT models and their main features:
Model | Technologies Used | Key Features and Benefits |
|---|---|---|
OptiXstar K572 | XGS-PON, Wi-Fi 7 | Very fast internet, strong performance, wide coverage |
EN8145B7Ns | XGS-PON, Wi-Fi 7 | Very fast internet, high speed, strong performance |
EN8245X6s-8N | XGS-PON, Wi-Fi 6 | Very fast internet, wide coverage |
EG8141X6-10 | GPON, Wi-Fi 6 | Smart routing ONT |
V166a-20 (Main FTTR) | GPON, Wi-Fi 6 | Very fast internet, wide coverage |
V261a-20 (Main FTTR) | GPON, Wi-Fi 7 | Very fast internet, wide coverage |
B866G-S2 (Main FTTR) | XGS-PON/GPON Combo | All-optical gigabit, good Wi-Fi for businesses |
Huawei ONT devices have many good points in fiber networks. They give very fast internet, up to 10 Gbps with XGPON. Multi-gigabit ports let many devices connect at once. This is great for big homes and offices. Security features like AES and RSA keep data safe from hackers.
Users say Wi-Fi works well, even in hard places. Dual-band Wi-Fi lets many devices work together with no lag. Voice ports make VoIP easy for talking. Huawei ONTs are stable and reliable, with little downtime. The simple interface makes setup and management easy.
Operators get smart network tools. Huawei’s home broadband solution cuts visits by 30%. It also makes fixing problems 20% faster. Fiber Iris helps find faults from far away, making repairs easier.
Huawei ONTs are better than other brands in many ways. The chart below shows ratings for Huawei, ZTE, and Nokia ONTs:
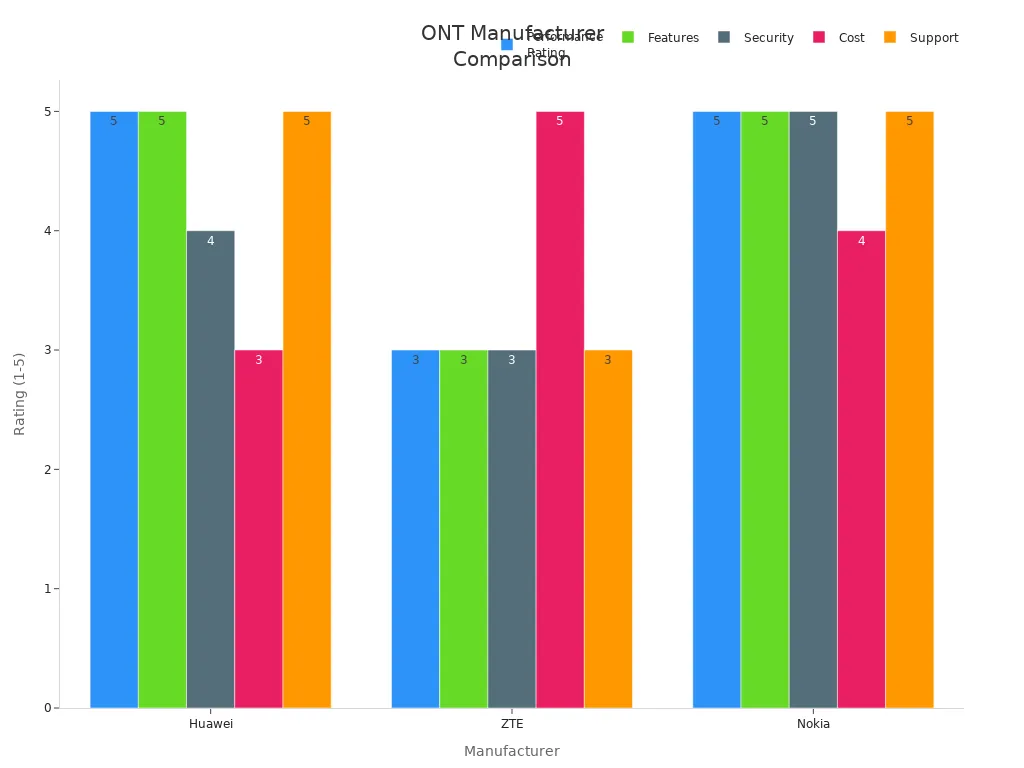
Huawei ONTs work well for video calls and cloud work. They fit into Huawei GPON systems for steady performance. Good customer support and updates keep devices safe and new. Wide Wi-Fi and future-ready tech make Huawei ONTs a top pick for homes and businesses.
Huawei ONT devices help carriers earn 40% more per user. They also cut costs by 30% with smart solutions like FTTR and FTTO 2.0.
The biggest differences between OLT, ONU, and ONT are what they do and where they are. OLT is found at the main office. It controls the whole network. ONU and ONT help connect people to the network. ONT is always inside the user’s home. The table below shows how each device is different:
Device | Role | Placement | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
OLT | Network control | Central office | Bandwidth management |
ONU | Signal conversion | Corridor or outside | May need extra parts |
ONT | User connection | Home | Direct device links |
People should think about what service they need. They should also look at where to put each device and how the network is set up. Huawei ONTs give fast internet, strong Wi-Fi, and are simple to use. Picking the right device helps keep fiber optic service working well.
OLT sits at the provider’s office and controls the network. ONU and ONT connect users. ONT usually serves one home. ONU can serve many users. Each device has a unique role in ONT GPON: OLT vs. ONU vs. ONT & Huawei ONT.
Yes, some networks use both. The ONU may serve as a shared point for several users. Each user then connects to an ONT inside their home. This setup appears in large buildings or business parks.
Huawei ONT offers fast Wi-Fi, strong security, and easy setup. Users get stable connections for video, gaming, and work. Smart management tools help operators fix problems quickly. Many models support the latest Wi-Fi standards.
ONT and ONU devices deliver high-speed internet, IPTV, and voice calls. Some models offer Wi-Fi, multiple Ethernet ports, and support for smart home devices. Users enjoy reliable streaming, online gaming, and clear phone calls.
Most ONT and ONU devices follow global standards. Many work with different brands of OLTs. Huawei ONT models often support both GPON and XGS-PON. Users should check compatibility before buying.